Mechanism charcoal is an environmentally friendly and efficient fuel, widely used in barbecue, industry and life heating. Its production process is mainly divided into five major steps: raw material treatment, rod making, carbonisation, cooling and packaging. The following are the specific processes:
- Raw material preparation
- Raw material selection: commonly used agricultural and forestry wastes (such as wood chips, straw, rice husk, tree branches, etc.).
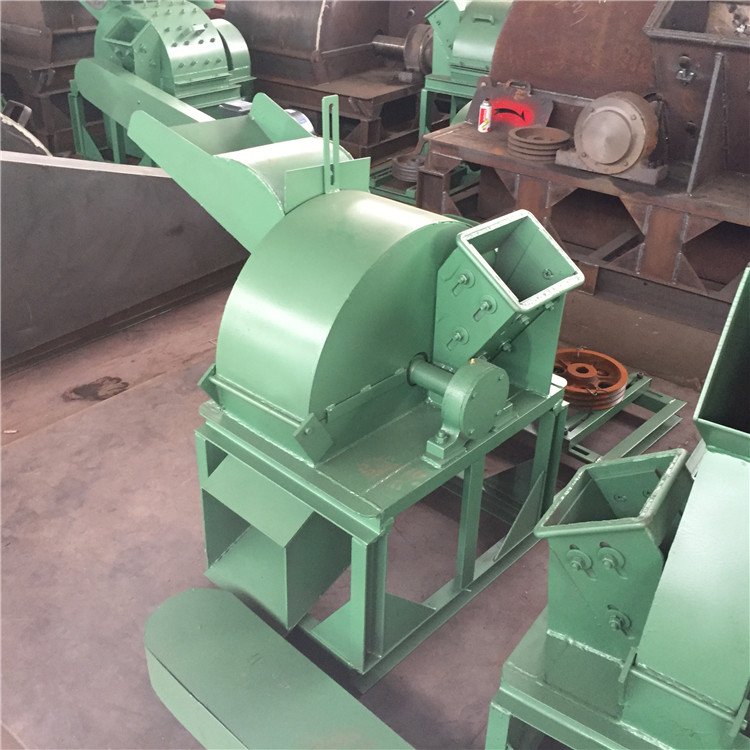
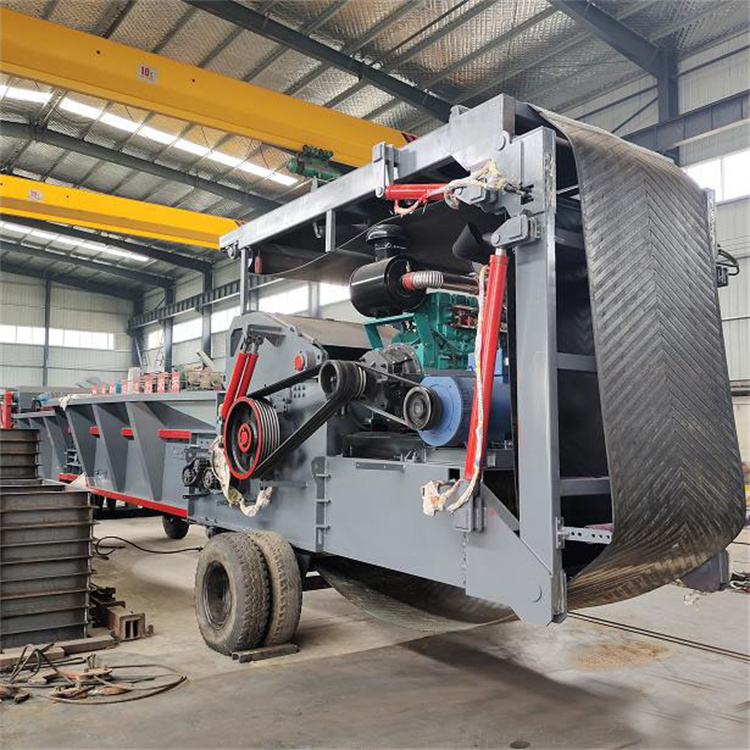
- Crushing: Process the raw materials into uniform powder or granule (particle size of about 3-5 mm) by crusher.
- Drying and dehumidification: Remove the moisture in the raw material by drying machine to reduce the moisture content to 10%-15% (for subsequent moulding).
- Rod moulding
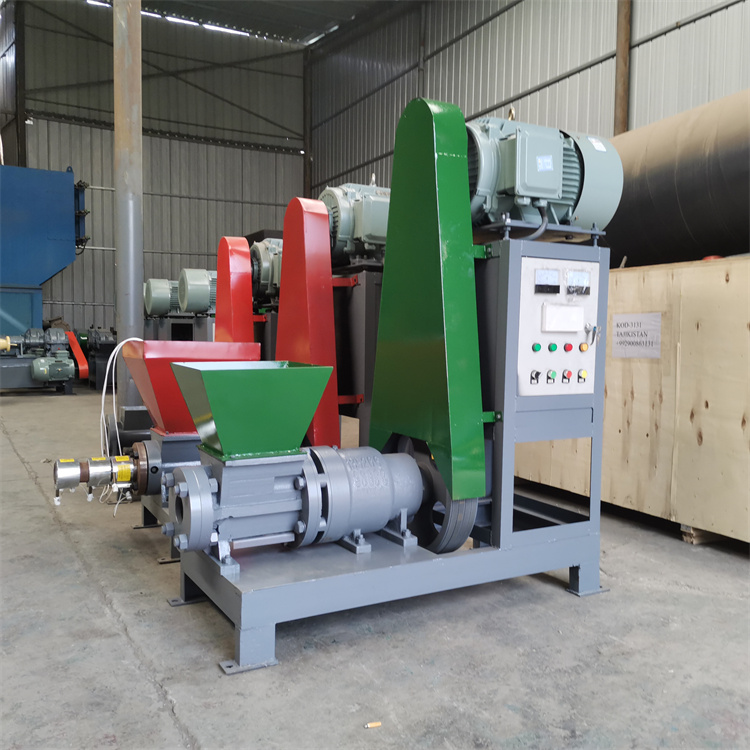
- Rod making machine extrusion: The dried raw materials are compressed into high-density square or hexagonal ‘charcoal rods’ (about 5-7 cm in diameter and adjustable in length) using a screw extruder to compress the well-mixed raw materials.
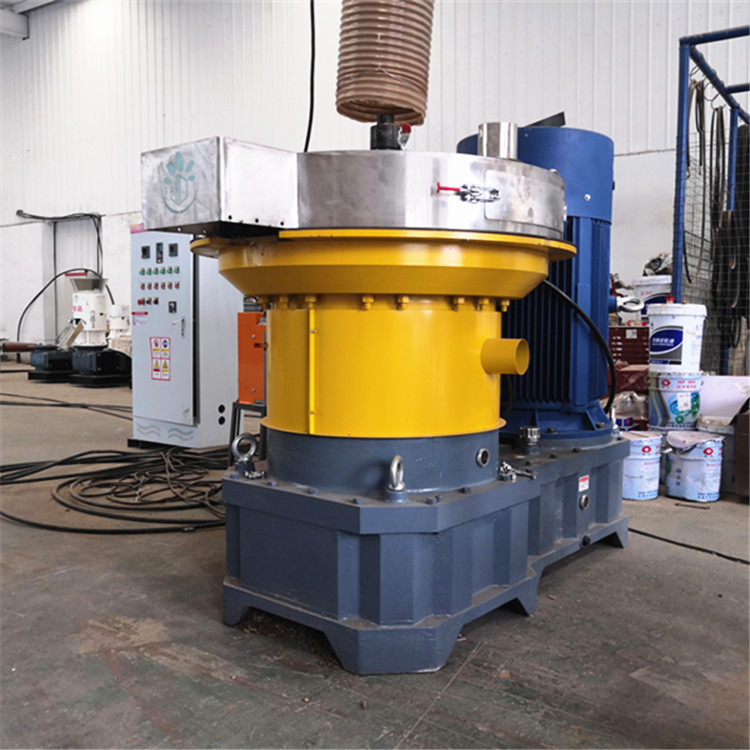
- Kiln loading and sealing: Charcoal sticks are loaded into the charring furnace (or kiln) and the door is sealed to control the entry of oxygen.
- Heating charring: The temperature inside the furnace is gradually increased to 300-600°C by external heating (e.g. burning biomass, wood, coal, diesel) for several hours.
- Low temperature stage (100-200°C): water evaporates and the raw material decomposes to produce volatile compounds (e.g. methane (which can be used as fuel for charring), carbon monoxide).
- High temperature stage (200-600°C): organic matter further decomposes to form fixed carbon (charcoal), while releasing tar and wood vinegar liquid.
- Cooling and quenching: after carbonisation is completed, the heat source is turned off and the fire is quenched either by natural cooling or by passing a small amount of air.
- Finished product processing
- Screening and grading: Remove the broken charcoal and impurities produced during the charring process, and grade them according to size.
- Surface treatment: wrapping environmentally friendly materials (such as paper packaging) to extend the preservation time.
- Quality inspection and packaging: check the calorific value, density, carbon content and other indicators of charcoal, qualified products are packed (commonly in bags or boxes).
Advantages of mechanism charcoal
- Environmental protection: utilisation of waste and reduction of deforestation; less soot and low CO₂ emission during combustion.
- High efficiency: high density, stable calorific value (about 7000-8000 kcal/kg), long burning time.
- Wide use: suitable for barbecue, metallurgy, chemical industry, agriculture (soil improvement) and other fields.
Precautions
- The charring temperature needs to be controlled in the production to avoid over-burning leading to charcoal ashing.
- The charring furnace needs to be equipped with waste gas treatment device to reduce pollution.
- Raw materials need to be fully dried, otherwise it will affect the quality of stick forming and carbonisation.
Through the above steps, mechanism charcoal realises the efficient transformation from waste material to high-quality fuel, which is both environmentally friendly and economic, and is a typical case of sustainable development.